The U.S. is currently facing a deadly outbreak of Legionnaire's Disease in different states including New York, California and Illinois.
The total number of confirmed cases in these states has already risen to hundreds with over a dozen reported deaths due to the fatal disease.
In California, the disease was detected at the San Quentin State Prison. Six inmates have already been confirmed to have been infected with the disease and another 95 individuals have already been placed under medical observations.
New York City, on the other hand, has been struggling with the outbreak for a couple of months now. According to NPR, since July of this year, around 124 cases of Legionnaire's disease have been reported in the South Bronx Area.
Various sources reported that traces of Legionella bacteria have been detected in the cooling tower of the Lincoln Hospital and the water supply of South Bronx's Melroses Houses. The outbreak has already claimed 12 lives in New York.
In Illinois, eight individuals have already died due to the disease and the state's number of confirmed cases has already reached 41. However, the Illinois Department of Public Health (IDPH) and Illinois Department of Veterans' Affairs (IDVA) believe that the number of those infected can still increase since the disease's incubation period can last up to two weeks.
"We remain vigilant in monitoring our residents and we continue to follow the guidance of our interagency partners to implement remediation efforts across our home," IDVA director Erica Jeffries said according to Pulse Headlines.
"The safety and quality of care for our residents and staff are our primary concerns," she added.
The government agency is currently monitoring the conditions of residents to see if new cases will emerge within the next weeks.
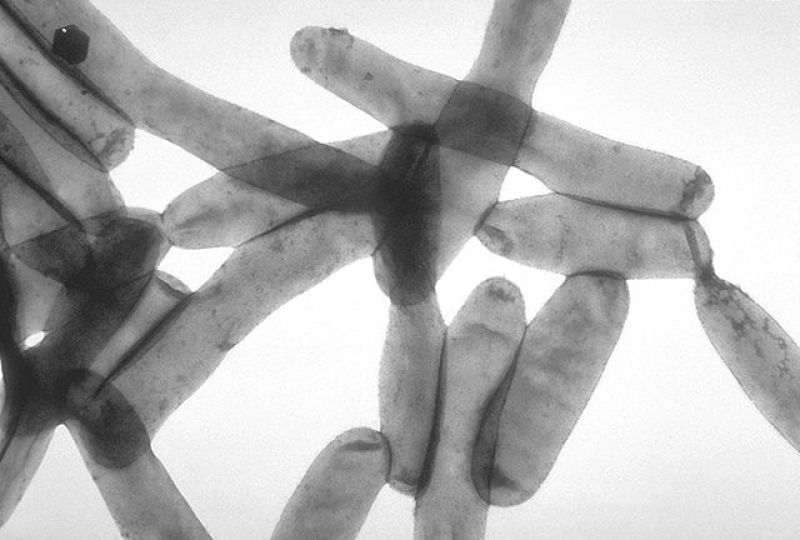
Legionnaire's Disease is caused by the Legionella bacteria and is categorized as a type of pneumonia. It thrives in water and can become airborne through steam and mist. This is primarily the reason why various states have already turned off the cooling towers, plumbing systems and steam-based heating mechanisms of various facilities to prevent the spread of the bacteria.
According to medical experts, those who are at risk of contracting the disease are smokers, people over 50 years old, those with lung ailments and people with weak immune systems. Some of the disease's symptoms include high fever, muscle pain, shortness of breath, coughing, chest pain, gastrointestinal issues and headaches, Nature World Report has learned.
Although the disease is considered fatal and does not yet have a preventive vaccine against it, it can be treated with the help of antibiotics.

















